2. 西南民族大学民族医药研究院, 四川 成都 610041
2. Ethnic Medicine Institute, Southwest University for Nationalities, Chengdu 610041, China
山豆根属Euchresta J. Benn植物是豆科(Fabaceae)中的一个小属,全世界共有4种3变种,分布于不丹、印度、印度尼西亚、日本、韩国、老挝、尼泊尔、菲律宾、泰国、越南及我国东南部至喜马拉雅。我国有4种2变种,分别为山豆根E. japonica Hook. f. ex Regel(A)、台湾山豆根E. formosana (Hayata) Ohwi (B)、伏毛山豆根E. horsfieldii (Lesch.) Benn.(C)、管萼山豆根E. tubulosa Dunn(D) [原变种E. tubulosa var. tubulosa、长序山豆根(变种)E. tubulosa Dunn var. longiracemosa (S. Lee & H. Q. Wen) C. Chen及短萼山豆根(变种)E. tubulosa Dunn var. brevituba C. Chen]。我国是该属的分布中心[1, 2],本属植物均为药用植物,主要含有黄酮类、生物碱类、甾类等成分,现代药理研究表明该属植物具有抗肿瘤、抗HIV活性、抗血小板聚集、中枢抑制、抗氧化、调血脂、抗菌等活性。为进一步研究开发该属植物,现对其国内外化学成分和生物活性研究成果进行分析。
1 化学成分山豆根属的现代研究始于20世纪30年代,迄今为止,报道的化学成分共有153种,其中黄酮类成分共86种,挥发油类40种,还含有部分生物碱类、少量的甾类及木酚素、叶绿素等其他成分。
1.1 黄酮类山豆根属植物中富含黄酮类成分,特别是异黄酮类,目前为止,已从该属植物中分到86个该类化合物(1~86)(表 1和图 1),其中包括37个异黄酮、24个黄酮,除trifolirhizin含糖苷,其他均以苷元形式存在。
| 表 1 从山豆根属植物分离得到的化合物 Table 1 Compounds isolated from plants in Euchresta J. Benn |
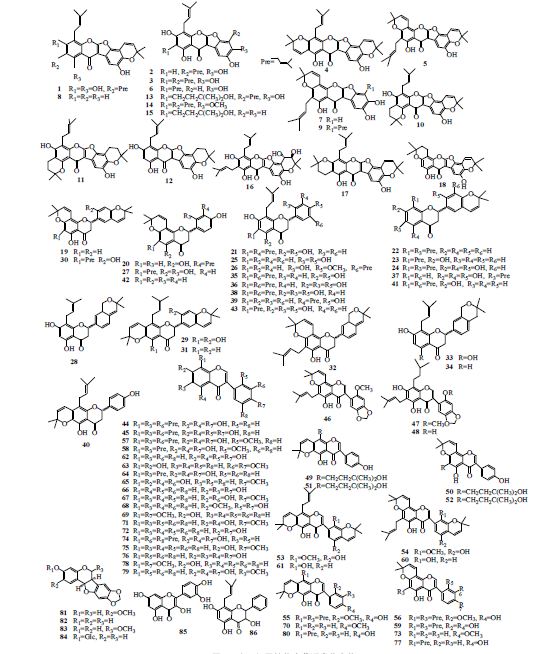 | 图 1 山豆根属植物中黄酮类化合物Fig. 1 Flavanoids isolated from plants of Euchresta J. Benn |
目前从该属植物中分离鉴定了苦参碱等14个生物碱类成分(87~100,表 1和图 2)。
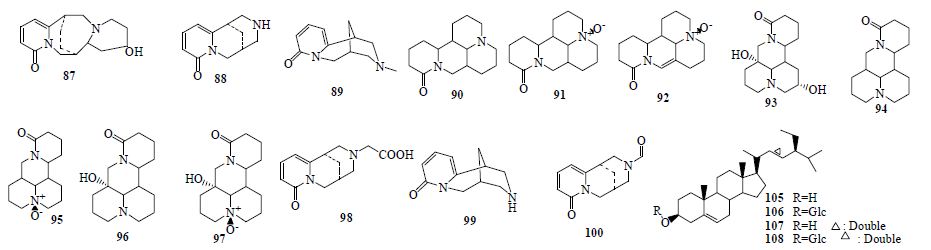 | 图 2 山豆根属植物生物碱类和甾体类化合物Fig. 2 Alkaloids and steroids in plants of Euchresta J. Benn |
共得到β-谷甾醇及其苷、β-豆甾醇及其苷等4个甾类成分(105~108,表 1和图 2)。
1.4 其他类除上述几类成分外,还分离得到苜蓿内酯、布卢门醇A、脱镁叶绿素及香兰素等9个化合物(101~104、109~113,表 1和图 3)。
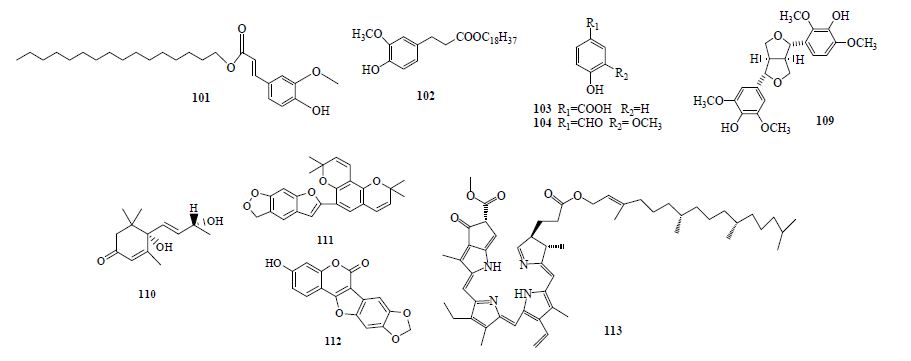 | 图 3 山豆根属植物其他类化合物Fig. 3 Other compounds isolated from plants of Euchresta J. Benn |
从伏毛山豆根中分离得到40种挥发性成分(114~153,表 1)。
2 生物活性山豆根属植物具有消炎、杀菌、消肿、止痛等功效,现代药理学研究表明山豆根属植物具有抗肿瘤、抗HIV、抗血小板聚集、中枢抑制、抗氧化、调血脂、抗菌等活性。
2.1 抗肿瘤在国内外,山豆根属多种植物民间都有用于治疗癌症的记载。20世纪五六十年代,日本学者新田五一[29]研究表明,山豆根对恶性肿瘤有显著效果,且副作用小。罗文利[30]进行细胞毒性实验,结果显示台湾山豆根中化合物1、10和13对人肝癌细胞59T有细胞毒作用,而化合物10对胃腺癌细胞SCM-1有细胞毒作用。通过实验研究台湾山豆根90%乙醇提取物(EFR)对人肝癌细胞Hep3B的影响表明,EFR可以降低Hep3B的存活率使Hep3B细胞周期停留在S期,并能诱发细胞凋亡[31]。同时能抑制Hep3B细胞中侵袭和转移相关的蛋白酶,抑制细胞外间质与基底膜的降解[32],抑制癌细胞的生长、成活和转移能力。
2.2 抗HIVLuo等[33]通过对台湾山豆根中一系列化合物抗HIV复制的检测表明,化合物13、17和74具有抑制HIV病毒在H9淋巴球中复制的作用。其EC50值分别为<0.100、<0.100和0.626 μg/mL,其治疗指数(TI)分别为>2.22、>2.18和3.90。
2.3 抗血小板凝集Luo等[33]通过对台湾山豆根中化合物抗血小板聚集的实验表明,在浓度100 μmol/L时,对花生四烯酸(AA)及胶原所诱发的血小板凝集,化合物79有完全抑制作用,化合物67有明显抑制作用。对胶原所诱发的血小板凝集,化合物76和66有完全抑制作用,化合物45、74、75、82和113有明显的抑制效果。化合物6对AA、胶原及血小板活化因子(PAF)所诱发的血小板凝集有明显抑制作用。上述化合物中,化合物6、79和67是最强的抗血小板凝集物质。
2.4 抗氧化Shizuo等[34]研究发现山豆根中分得的化合物64具有较强的抗氧化能力,且分子结构中含异戊烯基的抗氧化活性比不含异戊烯基者要强。王韵涵[35]用甲醇萃取台湾山豆根不同培植体诱导所得愈伤组织及悬浮细胞,进行萃取物DPPH自由基清除能力分析,结果显示在质量浓度为25 μg/mL时,均有90%以上的清除能力。
2.5 中枢抑制Lin等[36]研究发现台湾山豆根能通过影响大脑内5-羟色胺的释放降低室温情况下的大鼠体温。尹玉琴等[37]研究发现管萼山豆根中生物碱具有镇痛、镇静及降温等中枢抑制效能。蔡敏玲等[38]发现台湾山豆根的甲醇粗提物具有较好的镇痛作用。Chow等[39]发现台湾山豆根的水及乙醇粗提物具有较好的解热效果。
2.6 调血脂Kim等[40]研究发现伏毛山豆根无水乙醇提取物(EHX)能增加过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(PPAR)目标基因的表达,调节脂质代谢相关蛋白的表达,并指出EHX可以作为天然调脂剂。
2.7 抗菌、抗病毒经药理实验证明,化合物1在对抗大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、热带念珠菌方面具有比对羟基苯甲酰甲酯更强的抗菌活性[3]。王苑春等[41]发现台湾山豆根具有非常好的抗肠道病毒71型活性。
3 结语山豆根属植物在国内外享有较高声誉,爪哇岛当地居民公认伏毛山豆根为“药草中药效第一”;山豆根在日本民间用于抗癌和消炎、抗心律不齐、治疗溃疡;管萼山豆根为我国土家族聚集区“信誉极高的民族药”,对咽喉肿痛、牙痛、腹痛等痛症有“药到病除”的功效[42]。但现有的研究还存在许多不足。目前对山豆根、台湾山豆根的研究较多且较深入,对伏毛山豆根和管萼山豆根的研究较少;日本及中国台湾研究较为深入,中国大陆研究较为薄弱。
山豆根属植物传统应用以根茎部为主,叶部应用较少,已有研究发现,山豆根具有抗血小板聚集活性的成分来自于叶部,从综合开发和利用资源的角度,加强对叶部的研究是今后发展的方向。
今后应进一步加强对山豆根属植物的药理研究,尤其是抗肿瘤、抗HIV及抗血小板聚集等活性方面,阐明发挥作用的物质基础及机制,为新药的研发及人类医疗品质的改善服务。
| [1] | 中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志 (第42卷第2分册) [M]. 北京:科学出版社, 1993. |
| [2] | Wu Z Y, Hong D Y. Flora of China (10) [M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2010. |
| [3] | Mizuno M, Tamura K, Tanaka T, et al. A novel coumaronochromone from stems of Euchresta japonica [J]. Heterocycles, 1988, 26:2047-2050. |
| [4] | Mizuno M, Matsuura N, Iinuma, M, et al. Coumaronochromones in the roots Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1992, 30(2):643-664. |
| [5] | Mizuno M, Tanaka T, Tamura K I, et al. Coumaronochromones from the stems of Euchresta formosana [J]. Phytochemistry, 1989, 27(9):2418-2419. |
| [6] | Matsuura N, Iinuma, M, Tanaka T, et al. Flavanones and benzofuran in roots of Euchresta tubulosa [J]. Phytochemistry, 1993, 32(3):701-705. |
| [7] | Mizuno M, Matsuura N, Tanaka T, et al. Four flavanones in the roots Euchresta formosana [J]. Phytochemistry, 1991, 29(9):2995-2997. |
| [8] | Luo W L, Chang F R, Hsieh T J, et al. Coumaronochromonrs and flavanones from Euchresta formasana roots [J]. Phytochemistry, 2002, 60(8):839-845. |
| [9] | 罗文利. 台湾山豆根根茎与叶部化学成分及其生物活性之研究 [D]. 台北:高雄医学大学药学研究所, 2003. |
| [10] | Mizuno M, Tamura K I, Tanaka T, et al. Three prenylflavanones from Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1988, 26(6):1830-1833. |
| [11] | Mizuno M, Tamura K I, Tanaka T, et al. Chemotaxonomy of the genus Euchresta. III. Three new flavonoids in the roots Euchresta japonica [J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1989, 36:195-196. |
| [12] | Mizuno M, Tamura K I, Tanaka T. New prenylated flavonoids in Euchresta Japonica [A] // 16th International Symposium on the Chemistry of Natural Products [C]. Kyoto:International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1988. |
| [13] | Mizuno M, Tamura K I, Tanaka T, et al. Six flavanones from the roots Euchresta formosana [J]. Phytochemistry, 1989, 27(10):2711-2712. |
| [14] | Mizuno M, Tanaka T, Matsuura N, et al. Two flavanones from Euchresta horsfieldii [J]. Phytochemistry, 1990, 28(8):2638-2640. |
| [15] | Mizuno M, Tanaka T, Tamura K I, et al. Flavonoids in the roots Euchresta horsfieldii in Thailand [J]. Phytochemistry, 1990, 28(8):2563-65. |
| [16] | Matsuura N, Iinuma M, Mizuno M, et al. Chemotaxomic approach to the genus euchresta based on prenylflavonoids and prenylflavanones in the roots of Euchresta formosana [J]. Biochem Syst Ecol, 1995, 23:539-545. |
| [17] | Shirataki Y, Komatsu M, Yokoe I, et al. Studies on the constituents of Sophora species. XVI. Constituents of the roots of Euchresta japonica Hook. f. ex Regel [J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1981, 28:2932-2935. |
| [18] | Shirataki Y, Manaka A, Yokoe I, et al. Two prenylflavanones from Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1980, 21(12):2859-2863. |
| [19] | Mizuno M, Tamura K I, Tanaka T, et al. Prenylflavanones from Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1988, 26(9):2875-2877. |
| [20] | Mizuno M, Matsuura N, Iinuma M, et al. Isoflavanones from stems of Euchresta horsfieldii [J]. Phytochemistry, 1990, 28(8):2575-2577. |
| [21] | Mizuno M, Matsuura N, Iinuma M, et al. Isoflavanones from root of Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1992, 30(2):675-678. |
| [22] | Tanaka H, Doi M, Etoh H, et al. Revised structures for senegalensin and euchrenone b (10) [J]. J Nat Prod, 2001, 64:1326-1330. |
| [23] | Ohmiya S, Otomasu H, Haginiwa J. The alkaloid constituents of Euchresta japonica and the stereochemical assignment of two isomeric sophoridine N-oxide [J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1980, 27:546-551. |
| [24] | Ohmiya S, Otomasu H, Haginiwa J, et al. (-)-12-Cytisineacetic acid, a new lupin alkaloid in Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1979, 18(4):649-650. |
| [25] | Ohmiya S, Higashiyama K, Otomasu H, et al. (+)-5α, 9α-Dihydroxymatrine, a new lupin alkaloid from Euchresta horsfeldii [J]. Phytochemistry, 1979, 18(4):645-647. |
| [26] | 李若存, 候遇成. 管萼山豆根化学成分的研究--生物碱的分离鉴定 [J]. 湖南医药杂志, 1982, 9(1):51-53. |
| [27] | Ohmiya S, Otomasu H, Haginiwa J, et al. (+)-5, 17-Dehydromatrine N-oxide, a new alkaoid in Euchresta japonica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1978, 17(11):2021-2022. |
| [28] | Tirta I G, Ardaka I M, Dw D I, et al. Study on phenology and chemical compound of pronojiwo (Euchresta horsfieldii (Lesch.) Benn.) [J]. Bull Littro, 2010, 21(1):28-36. |
| [29] | 新田五一. 山豆根抑制恶性肿瘤的研究 [J]. 日本东洋医学会志, 1959, 10(2):1-14. |
| [30] | Luo W L, Chang R, Liaw C C, et al. Cytotoxic coumaronochromones from the roots of Euchresta formosana [J]. Planta Med, 2002, 68(2):146-151. |
| [31] | Hsu S C, Kuo C L, Lin J P, et al. Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana radix induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (Hep3B) [J]. Anticancer Res, 2007, 26(4B):2305-2314. |
| [32] | Hsu S C, Kuo C L, Lin J P, et al. Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana radix inhibit invasion and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Anticancer Res, 2007, 26(4B):2367-2384. |
| [33] | Luo W L, Wu C C, Chang F R, et al. Antiplatelet and anti-HIV constituents from Euchresta formosana [J]. Nat Prod Res, 2003, 17(2):91-97. |
| [34] | Shizuo T, Yoshiaki S. Inhibitory effect of prenylated flavonoid in Euchresta japonica and Artocarpus heterophyllus on lipid peroxidation by interaction of hemoglobin and hydrogen peroxide [J]. Pharm Biol, 2006, 44(4):261-263. |
| [35] | 王韵涵. 台湾山豆根组织培养及其抗氧化能力评估 [D]. 台北:大同大学, 2013. |
| [36] | Lin M T, Chi M L, Han P W. Effects of Shan-dou-gen (Euchresta formosana) on metabolic, respiratory and vasomotor activities as well as body temperature in rats [J]. Am J Chin Med, 1980, 8(1/2):96-103. |
| [37] | 尹玉琴, 何汉增, 袁惠南, 等. 管萼山豆根药理作用的实验研究--管萼山豆根总生物碱对中枢神经系统作用的初步观察 [J]. 湖南医药杂志, 1984(5):49-52. |
| [38] | 蔡敏玲. 台湾市售山豆根类药材之生药学研究 [M]. 台中:中国医药学院中国药学研究所, 1995. |
| [39] | Chow S Y, Chen S M, Yang J C. Pharmacological studies on Chinese herbs. (5) Antipyretic effects of 12 Chinese herbs [J]. J Formosan Med Assoc, 1997, 76(4):338-343. |
| [40] | Kim J H, Kim D, Kim J, et al. Euchresta horsfieldii Benn. activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and regulates expression of genes involved in fatty acid metabolism in human HepG2 cells [J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2011, 132(1):233-237. |
| [41] | 王苑春. 大本山葡萄抗肠病毒活性及活性成分之研究 [D]. 台中:中兴大学, 2011. |
| [42] | 李厚聪, 袁德培, 袁成玉. 土家族濒危药物胡豆莲的研究进展 [J]. 湖北民族学院学报:医学版, 2011, 28(4):71-73. |
 2014, Vol. 45
2014, Vol. 45
