2. 天津药物研究院, 天津 300193;
3. 中药现代制剂与质量控制技术国家地方联合工程实验室, 天津 300193;
4. 甘肃陇神戎发药业股份有限公司, 甘肃 兰州 730101
2. Tianjin Institute of Pharmaceutical Research, Tianjin 300193, China;
3. National & Local United Engineering Laboratory of Modern Preparation and quality control Technology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China;
4. Gansu Long-Shen-Rong-Fa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Lanzhou 730101, China
元胡止痛方由中药醋延胡索与白芷组成,方中君药延胡索为罂粟科植物延胡索Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang的干燥块茎,辛温通散,为行气活血、止痛良药,善治一身上下诸痛;臣药白芷为伞形科植物白芷Angelica dahurica (Fisch. ex Hoffm.) Benth. et Hook. f. 或杭白芷Angelica
dahurica (Fisch. ex Hoffm.) Benth. et Hook. f. var. formosana (Boiss.) Shan et Yuan的干燥根,可散风寒、宣湿痹、行气血以除头痛、身痛。两药相须为用,具有理气、活血、止痛的作用,用于治疗气滞血瘀引起的胃痛、头痛、肋痛及痛经[1]。该方组方精炼,疗效确切,临床应用广泛。迄今为止,已报道元胡止痛方中延胡索和白芷含有的化学成分有生物碱类、香豆素类、酚酸类和萜类等,且具有显著的镇痛活性。本文对国内外有关元胡止痛方、延胡索和白芷的文献资料进行系统的整理,对其化学成分及药理作用研究进展进行全面综述,以期为元胡止痛方的药效物质基础研究提供参考。1 化学成分
1.1 生物碱类
生物碱为元胡止痛方镇痛作用的主要活性成分。目前从延胡索和白芷中分离得到并经过结构鉴定的生物碱类成分共65种(表 1和图 1),其中广金钱草碱(64)来自于白芷,其他生物碱类均来自于延胡索中,且以原小檗碱和阿朴啡类生物碱成分居多。原小檗碱类生物碱可以看成2个异喹啉环稠合而成,其中包含延胡索乙素(1)等叔胺碱和小檗碱(18)等季铵碱。阿朴啡类生物碱也具有异喹啉的基本母核,且含有部分饱和的菲核,包含海罂粟碱(35)等叔胺碱。
| 表 1 元胡止痛方中生物碱类化学成分 Table 1 Alkaloids from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
 | 图 1 元胡止痛方中生物碱类化学成分结构Fig. 1 Structures of alkaloids isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
香豆素为元胡止痛方抗炎镇痛及对心血管作用的主要活性成分之一。目前从元胡止痛方中分离得到并经过结构鉴定的香豆素类成分共97种(表 2和图 2),均来自于白芷,其中以欧前胡素(66)等线型呋喃香豆素居多,共53种,且多为C-5, 8位取代,此外还含有线型二氢香豆素、角型香豆素、角型二氢香豆素、简单香豆素等。白芷香豆素类成分部分以苷类形式存在,如紫花前胡苷(125),多为香豆素母核侧链上的叔碳或仲碳与葡萄糖、芹糖等呈苷键结合的单糖、二糖苷。
| 表 2 元胡止痛方中香豆素类化学成分 Table 2 Coumarins isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
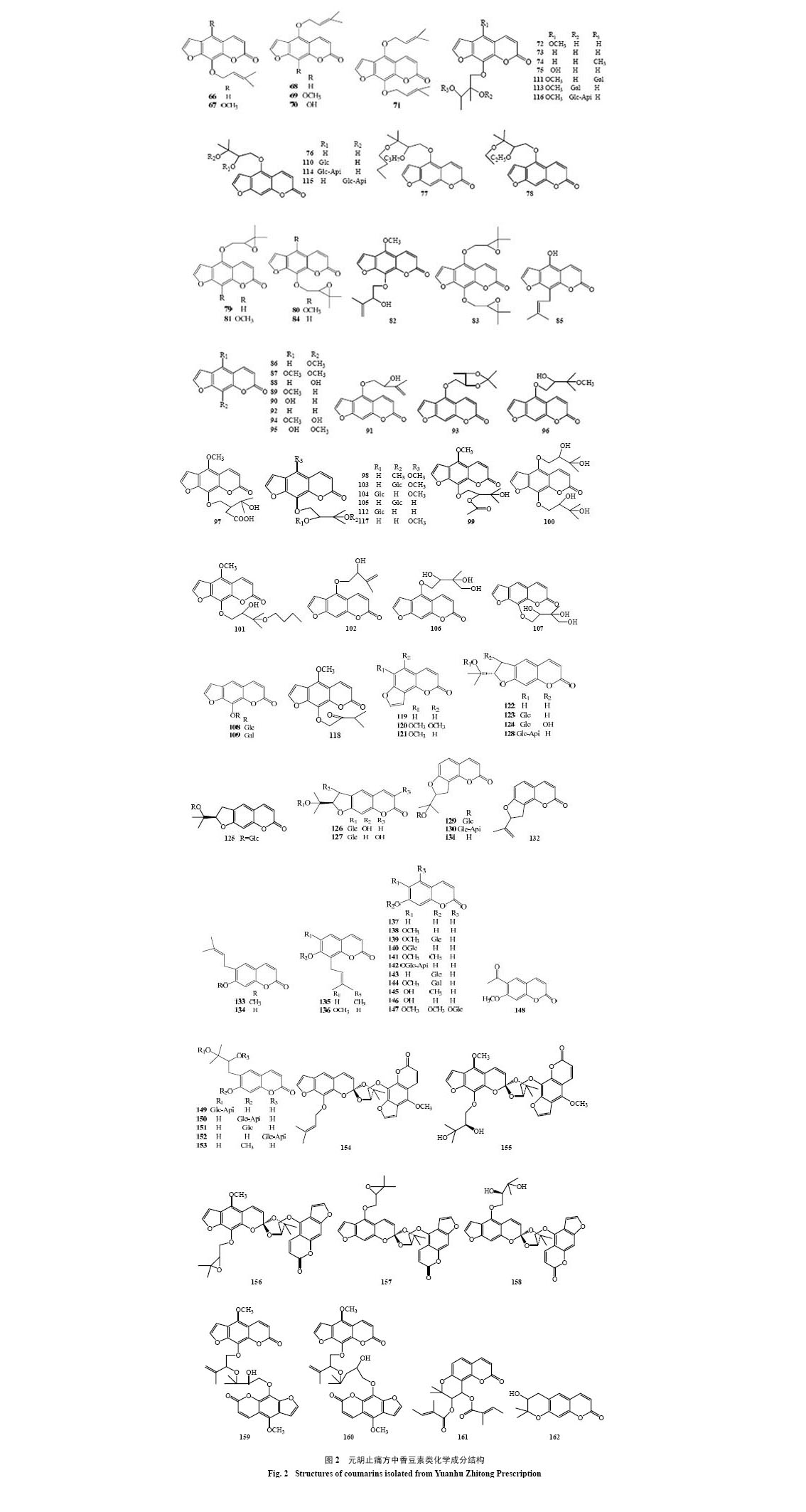 | 图 2元胡止痛方中香豆素类化学成分结构Fig. 2 Structures of coumarins isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
元胡止痛方中尚含有酚酸类成分,目前分离得到并经过结构鉴定的共13种(表 3及图 3),其中山嵛酸(163)、香草酸(164)、对羟基苯甲酸(165)、大黄素(169)、大黄素甲醚(170)来自于延胡索,其他化合物均来自于白芷。
| 表 3 元胡止痛方中酚酸类化学成分 Table 3 Phenolic acids isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
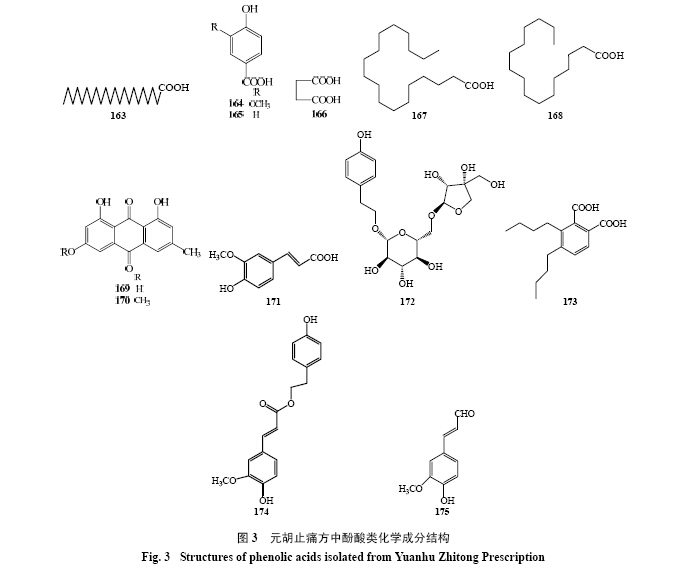 | 图 3元胡止痛方中酚酸类化学成分结构Fig. 3 Structures of phenolic acids isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
1.4 甾体及三萜类
元胡止痛方中还含有较少的甾体及三萜类成分。目前分离得到的甾体成分共4种,即β-谷甾醇(176)、β-胡萝卜苷(177)、豆甾醇(178)、麦角甾-4-烯-3-酮(180),其中麦角甾-4-烯-3-酮(180)来自延胡索,其他成分为延胡索及白芷所共有;三萜类成分1种,即3β-羟基-齐墩果烷-11,13(18)-二烯- 28-酸(179),来自于延胡索。目前从元胡止痛方中已分离得到的甾体及三萜类化合物及结构式见表 4及图 4。
| 表 4 元胡止痛方中甾体及三萜类化学成分 Table 4 Steroides and triterpenes isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
 | 图 4元胡止痛方中甾体及三萜类化学成分结构Fig. 4 Structures of steroides and triterpenes isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
挥发油类成分为元胡止痛方抗菌消炎、镇痛作用的主要活性成分之一,该方所含挥发油类大部分来自于白芷,少量来自于延胡索。由于药材生长地理环境不同及加工存贮过程中挥发油易氧化等因素导致白芷中挥发油成分种类较多。聂红等[78]研究发现白芷挥发油中以甲基-环癸烷等饱和烃类的量最高,其次为醇类、不饱和烃等成分。赵爱红等[79]研究发现白芷根中挥发油类成分主要含有3-蒈烯(12.70%)、β-榄香烯(6.20%)、β-松油烯(3.53%)、β-香叶烯(1.97%)等。
1.6 其他成分
研究发现元胡止痛方中除上述成分外还含有醌类、烃类等其他成分,以及糖类、氨基酸、矿物元素等成分,其中N,N-二甲基-N′,N′-二甲基-二苯基酮(181)及N,N-二甲基-N′-甲基-二苯基酮(182)来自于延胡索,补骨脂醌(183)等其他成分主要来自于白芷。目前从元胡止痛方中已分离得到的其他化合物及结构式见表 5及图 5。
| 表 5 元胡止痛方中其他类化学成分 Table 5 Other chemical constituents isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
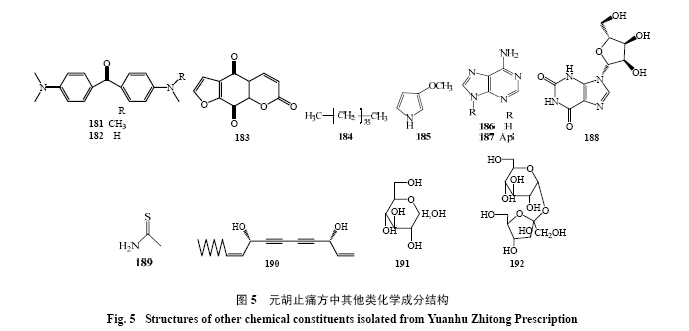 | 图 5元胡止痛方中其他类化学成分结构Fig. 5 Structures of other chemical constituents isolated from Yuanhu Zhitong Prescription |
2 药理作用
现代药理研究表明,元胡止痛方总提取物及其有效部位如生物碱类、香豆素类及挥发油等具有广泛的药理活性,包括镇痛、舒张血管以及平滑肌解痉等。
2.1 镇痛作用
研究表明元胡白芷配方药液对大鼠痛经及福尔马林疼痛模型镇痛作用明显,且对外周血中前列腺素、单胺类及β-内啡肽有显著影响,其作用具有多靶点的特点[80]。陈岳涛等[81]研究发现元胡止痛片对痛经模型大鼠有显著镇痛效果,可能为延胡索乙素与欧前胡素协同作用。欧前胡素镇痛机制可能与提高超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,降低丙二醛(MDA)量有关,但延胡索乙素通过何种途径与欧前胡素产生协同作用有待进一步研究。研究发现元胡止痛方的镇痛活性物质基础主要为延胡索乙素、白芷总香豆素及挥发油类。
2.2 对心血管系统的作用
元胡止痛方的大鼠肠吸收液具有显著的血管舒张活性,且存在量-效和时-效关系[82]。白芷中香豆素类化合物具有舒张动脉血管、改善血液循环等作用[83]。延胡索乙素体外具有抑制血小板聚集作用[84]。
2.3 解痉及其他药理作用
研究表明元胡止痛胶囊含药血清对大鼠离体子宫收缩具有解痉作用[85]。白芷总香豆素能对抗BaCl2所致兔肠平滑肌痉挛,具有明显的解痉作用[86]。此外,元胡止痛方还具有抗胃溃疡、抗病原微生物以及抗肿瘤等多种药理活性。
3 结语
元胡止痛方的化学成分与延胡索、白芷单味药材所含成分基本一致,而该方通过药物配伍可对主要化学成分的溶出、吸收等产生影响。研究发现,延胡索与白芷配伍后延胡索乙素的溶出量较单味药提高[87];将延胡索分别与白芷、当归进行配伍研究,发现延胡索与白芷配伍后总生物碱溶出量较高[88]。考察延胡索与白芷有效组分配伍后对延胡索乙素小肠吸收的影响,发现在一定配比范围内,延胡索总碱中延胡索乙素的小肠吸收呈显著增加的趋势[89]。白芷香豆素分子中具内酯结构,碱性条件下会水解开环;有的还含有酯基,尤其是取代侧链上的酯基极易发生碱水解,故元胡止痛成方制剂中多将延胡索与白芷2味药材分别提取。
方剂的化学成分和药效物质基础的研究是复方中药现代化研究的基础。元胡止痛方化学成分复杂, 本文综述了已报道的192个成分,包括生物碱类、香豆素类、酚酸类和萜类等,各成分通过不同的作用机制发挥镇痛、解痉等药效作用。同时,作为一个整体,复方中药物质群中各成分通过各种方式的协同发挥多靶点、多途径、多层次的整体功效。迄今为止,虽然已有大量关于延胡索和白芷2味药材的化学成分和药理学研究报道,但关于元胡止痛方的深入研究仍然存在较大的空间。因此,运用现代化学和生命科学领域的新技术和新方法对元胡止痛方的镇痛药效物质基础及作用机制进行归纳、总结和深入研究,将进一步阐释该方的药效物质基础、作用机制和临床价值,并为该方的质量控制及临床合理运用提供理论依据。
| [1] | 中国药典 [S]. 一部. 2010. |
| [2] | Shi J M, Han W L, Ye W C, et al. Phytochemical Investigation of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2011, 23(2): 647-651. |
| [3] | 吕子明, 孙武兴, 段绪红, 等. 延胡索化学成分研究 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(2): 235-237. |
| [4] | Liu Z L, Yu Y, Shen P N, et al. Separation and purification of dl-tetrahydropalmatine from Corydalis yanhusuo by high-speed counter-current chromatography [J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2008, 58(3): 343-346. |
| [5] | Zhang S J, Wang X L, Ouyang F, et al. Separation and purification of dl-tetrahydropalmatine from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang by HSCCC with a new solvent system screening method [J]. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 2008, 31(17): 2632-2642. |
| [6] | Zhai Z D, Shi Y P, Wu X M, et al. Chiral high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of the enantiomers of tetrahydropalmatine and tetrahydro-berberine, isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 384(4): 939-945. |
| [7] | Tong S Q, Yu Q, Li X N, et al. Preparative separation of tertiary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang by pH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography [J]. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 2013, 36(2): 229-238. |
| [8] | Xiao H T, Peng J, Liang Y, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Nat Prod Res, 2011, 25(15): 1418-1422. |
| [9] | Ma Z Z, Xu W, Jensen N H, et al. Isoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo and their binding affinities at the dopamine D (1) receptor [J]. Molecules, 2008, 13(9): 2303-2312. |
| [10] | 王丽丽. 植物延胡索化学成分的研究 [D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2010. |
| [11] | 白 雪, 肖海涛, 杨 杰, 等. 延胡索中紫堇碱标准品的制备及含量测定 [J]. 时珍国医国药, 2009, 20(2): 374-375. |
| [12] | 张晓丽, 曲 扬, 侯家鸣, 等. 延胡索的化学成分 [J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2008, 25(7): 537-540. |
| [13] | 胡甜甜. 延胡索的化学成分和生物活性研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2009. |
| [14] | 冯 静, 于宗渊, 杨洪军, 等. 延胡索中生物碱成分的研究 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013, 19(6): 124-127. |
| [15] | Fu X Y, Liang W Z, Tu G S, et al. Chemical studies on the alkaloids isolated from the tuber of Yuanhu (Corydalis turtschaninovii Bees. f. yanhusuo Y. H. Chou et C. C. Hsu) [J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 1986, 21(6): 447-453. |
| [16] | 丁 波. 延胡索物质基础及主要活性单体体内代谢的LC-DAD-MS/MS研究 [D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2007. |
| [17] | 程星烨, 石 钺, 郑顺亮, 等. 延胡索抗心肌缺血有效部位化学成分研究 [J]. 中药材, 2008, 31(11): 1656-1658. |
| [18] | 周 琼. 延胡索化学成分研究及其中草药特色体系化学特征表达 [D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2012. |
| [19] | 崔 征, 齐美玲, 殷 军, 等. 东北延胡索的化学成分及近缘植物的植物化学分类学 [C]. 北京: 中国植物学会七十五周年年会论文摘要汇编, 2008. |
| [20] | 许翔鸿, 王铮涛, 余国奠, 等. 延胡索中生物碱成分的研究 [J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2002, 33(6): 483-486. |
| [21] | 国家中医药管理局. 中药大辞典 [M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2012. |
| [22] | Jong K L, Jin G C, Myoung C S, et al. Isolation of isoquinoline alkaloids from the tuber of Corydalis turtschaninovii and their inhibition activity on low density lipoprotein oxidation [J]. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem, 2009, 52(6): 646-654. |
| [23] | 张晓丽. 延胡索的化学成分研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2008. |
| [24] | Hu T T, Zhang X, Ma S Z, et al. Chemical constituents from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Chin J Chin Mater Med, 2009, 34(15): 1917-1920. |
| [25] | 杨鑫宝, 刘扬子, 杨秀伟, 等. 磐安延胡索的化学成分研究 [J]. 中草药, 2013, 44(16): 2200-2207. |
| [26] | 王文蜀, 肖 巍, 喻 蓉, 等. 中药延胡索化学成分研究 [J]. 中央民族大学学报, 2007, 16(1): 80-86. |
| [27] | Wang C R, Guo Z M, Zhang J, et al. High-performance purification of quaternary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang using a new polar-copolymerized stationary phase [J]. J Sep Sci, 2011, 34(1): 53-58. |
| [28] | Zhang J, Jin Y, Liu Y F, et al. Purification of alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang using preparative 2-D HPLC [J]. J Sep Sci, 2009, 32(9): 1401-1406. |
| [29] | 刘 川. 江苏元胡块茎中化学成分的研究 [J]. 中国药科大学学报, 1989, 20(5): 261-265. |
| [30] | Hu T T, Zhang X, Ma S Z, et al. A new protoberberine alkaloid from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang [J]. Chin Chem Lett, 2009, 20(8): 955-957. |
| [31] | Cheng X Y, Shi Y, Zheng S L, et al. Two new protoberberine quaternary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2008, 10(12): 1117-1121. |
| [32] | 中国药典 [S]. 一部. 2010. |
| [33] | Shi J M, Han W L, Ye W C, et al. Phytochemical Investigation of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Nat Prod Res Dev, 2011, 23(2): 647-651. |
| [34] | 吕子明, 孙武兴, 段绪红, 等. 延胡索化学成分研究 [J]. 中国中药杂志, 2012, 37(2): 235-237. |
| [35] | Liu Z L, Yu Y, Shen P N, et al. Separation and purification of dl-tetrahydropalmatine from Corydalis yanhusuo by high-speed counter-current chromatography [J]. Sep Purif Technol, 2008, 58(3): 343-346. |
| [36] | Zhang S J, Wang X L, Ouyang F, et al. Separation and purification of dl-tetrahydropalmatine from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang by HSCCC with a new solvent system screening method [J]. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 2008, 31(17): 2632-2642. |
| [37] | Zhai Z D, Shi Y P, Wu X M, et al. Chiral high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of the enantiomers of tetrahydropalmatine and tetrahydro-berberine, isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2006, 384(4): 939-945. |
| [38] | Tong S Q, Yu Q, Li X N, et al. Preparative separation of tertiary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang by pH-zone-refining counter-current chromatography [J]. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 2013, 36(2): 229-238. |
| [39] | Xiao H T, Peng J, Liang Y, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Nat Prod Res, 2011, 25(15): 1418-1422. |
| [40] | Ma Z Z, Xu W, Jensen N H, et al. Isoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Corydalis yanhusuo and their binding affinities at the dopamine D (1) receptor [J]. Molecules, 2008, 13(9): 2303-2312. |
| [41] | 王丽丽. 植物延胡索化学成分的研究 [D]. 延吉: 延边大学, 2010. |
| [42] | 白 雪, 肖海涛, 杨 杰, 等. 延胡索中紫堇碱标准品的制备及含量测定 [J]. 时珍国医国药, 2009, 20(2): 374-375. |
| [43] | 张晓丽, 曲 扬, 侯家鸣, 等. 延胡索的化学成分 [J]. 沈阳药科大学学报, 2008, 25(7): 537-540. |
| [44] | 胡甜甜. 延胡索的化学成分和生物活性研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2009. |
| [45] | 冯 静, 于宗渊, 杨洪军, 等. 延胡索中生物碱成分的研究 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2013, 19(6): 124-127. |
| [46] | Fu X Y, Liang W Z, Tu G S, et al. Chemical studies on the alkaloids isolated from the tuber of Yuanhu (Corydalis turtschaninovii Bees. f. yanhusuo Y. H. Chou et C. C. Hsu) [J]. Acta Pharm Sin, 1986, 21(6): 447-453. |
| [47] | 丁 波. 延胡索物质基础及主要活性单体体内代谢的LC-DAD-MS/MS研究 [D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2007. |
| [48] | 程星烨, 石 钺, 郑顺亮, 等. 延胡索抗心肌缺血有效部位化学成分研究 [J]. 中药材, 2008, 31(11): 1656-1658. |
| [49] | 周 琼. 延胡索化学成分研究及其中草药特色体系化学特征表达 [D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2012. |
| [50] | 崔 征, 齐美玲, 殷 军, 等. 东北延胡索的化学成分及近缘植物的植物化学分类学 [C]. 北京: 中国植物学会七十五周年年会论文摘要汇编, 2008. |
| [51] | 许翔鸿, 王铮涛, 余国奠, 等. 延胡索中生物碱成分的研究 [J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2002, 33(6): 483-486. |
| [52] | 国家中医药管理局. 中药大辞典 [M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2012. |
| [53] | Jong K L, Jin G C, Myoung C S, et al. Isolation of isoquinoline alkaloids from the tuber of Corydalis turtschaninovii and their inhibition activity on low density lipoprotein oxidation [J]. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem, 2009, 52(6): 646-654. |
| [54] | 张晓丽. 延胡索的化学成分研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2008. |
| [55] | Hu T T, Zhang X, Ma S Z, et al. Chemical constituents from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Chin J Chin Mater Med, 2009, 34(15): 1917-1920. |
| [56] | 杨鑫宝, 刘扬子, 杨秀伟, 等. 磐安延胡索的化学成分研究 [J]. 中草药, 2013, 44(16): 2200-2207. |
| [57] | 王文蜀, 肖 巍, 喻 蓉, 等. 中药延胡索化学成分研究 [J]. 中央民族大学学报, 2007, 16(1): 80-86. |
| [58] | Wang C R, Guo Z M, Zhang J, et al. High-performance purification of quaternary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang using a new polar-copolymerized stationary phase [J]. J Sep Sci, 2011, 34(1): 53-58. |
| [59] | Zhang J, Jin Y, Liu Y F, et al. Purification of alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang using preparative 2-D HPLC [J]. J Sep Sci, 2009, 32(9): 1401-1406. |
| [60] | 刘 川. 江苏元胡块茎中化学成分的研究 [J]. 中国药科大学学报, 1989, 20(5): 261-265. |
| [61] | Hu T T, Zhang X, Ma S Z, et al. A new protoberberine alkaloid from Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang [J]. Chin Chem Lett, 2009, 20(8): 955-957. |
| [62] | Cheng X Y, Shi Y, Zheng S L, et al. Two new protoberberine quaternary alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2008, 10(12): 1117-1121. |
| [63] | Zhou Q, Deng A J, Qin H L, et al. Two new quaternary protoberberine alkaloids from Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. J Asian Nal Prod Res, 2012, 14(5): 476-481. |
| [64] | Lei Y, Tan J, Wink M, et al. An isoquinoline alkaloid from the Chinese herbal plant Corydalis yanhusuo W. T. Wang inhibits P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance-associate protein 1 [J]. Food Chem, 2012, 136(34): 1117-1121. |
| [65] | 傅小勇, 梁文藻, 徐国士. 元胡块茎中生物碱的化学研究 [J]. 药物分析杂志, 1986, 6(1): 6-9. |
| [66] | 傅小勇, 梁文藻, 徐国士. 延胡索生物碱的化学研究—VII 元胡块茎中的生物碱 [J]. 中草药, 1986, 17(12): 533-534. |
| [67] | 卢 嘉, 金 丽, 金永生, 等. 中药杭白芷化学成分的研究 [J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2007, 28(3): 294-298. |
| [68] | Wei Y, Ito Y. Preparative isolation of imperatorin, oxypeucedanin and isoimperatorin from traditional Chinese herb ""bai zhi"" Angelica dahurica (Fisch ex Hoffm) Benth. et Hook using multidimensional high-speed counter-current chromatography [J]. J Chromatogr A, 2006, 1115(12): 112-127. |
| [69] | Yun W, Ito Y. Isolation of imperatorin, oxypeucedanin, and isoimperatorin from Angelica dahurica (Fisch ex Hoffm) Benth. et Hook by stepwise flow rate high-speed countercurrent chromatography [J]. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol, 2006, 29(11): 1609-1618. |
| [70] | Wang T T, Jin H, Li Q, et al. Isolation and simultaneous determination of coumarin compounds in Radix Angelica dahurica [J]. Chromatographia, 2007, 65(78): 477-481. |
| [71] | Bergendorff O, Dekermendjian K, Nielsen M, et al. Furanocoumarins with affinity to brain benzodiazepine receptors in vitro [J]. Phytochemistry, 1997, 44(6): 1121-1124. |
| [72] | Kimura Y, Okuda H. Histamine-release effectors from Angelica dahurica var. dahurica root [J]. J Nat Prod, 1997, 60(3): 249-251. |
| [73] | 王正帅. 白芷化学成分及质量标准研究 [D]. 郑州: 河南大学, 2005. |
| [74] | 王梦月. 白芷的古今药用概况及香豆素类成分研究 [D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2003. |
| [75] | 王梦月, 贾敏如, 马逾英, 等. 白芷镇痛有效部位的化学成分研究 [J]. 中国药学杂志, 2005, 40(8): 583-585. |
| [76] | 孙振蛟. 浙江产杭白芷化学成分及总香豆素类成分提取工艺的研究 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳药科大学, 2004. |
| [77] | 周爱民, 李 强, 雷海民, 等. 白芷化学成分的研究 [J]. 中草药, 2010, 41(7): 1081-1083. |
| [78] | Zhao A, Yang X, Yang X, et al. A new natural product from root of Angelica dahurica cv. Qibaizhi [J]. Chin J Chin Mater Med, 2012, 37(16): 2400-2407. |
| [79] | Kim Y K, Kim Y S, Ryu S Y. Antiproliferative effect of furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica on cultured human tumor cell lines [J]. Phytother Res, 2007, 21(3): 288-290. |
| [80] | 赵爱红, 杨秀伟. 兴安白芷脂溶部位中新的天然产物 [J]. 中草药, 2014, 45(13): 1820-1828. |
| [81] | Baek N I, Ahn E M, Kim H Y, et al. Furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica [J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2000, 23(5): 467-470. |
| [82] | 贾晓东, 赵兴增, 冯 煦, 等. 杭白芷香豆素类成分的研究 [J]. 中草药, 2008, 39(12): 1768-1771. |
| [83] | 张如意, 张建华, 王 洋, 等. 白芷化学成分的分离和鉴定 [J]. 北京医学院学报, 1985, 17(2): 103-104. |
| [84] | Marumoto S, Miyazawa M. β-Secretase inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica [J]. Phytother Res, 2010, 24(4): 510-513. |
| [85] | Saiki Y, Morinaaga K, Okegawa O, et al. On the coumarins of the roots of Angelica dahurica Benth. et Hook [J]. Yakugaku Zasshi, 1971, 91(12): 1313-1317. |
| [86] | 陈 军. 茅苍术和白芷化学成分研究 [D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2007. |
| [87] | Piao X L, Yoo H H, Kim H Y, et al. Estrogenic activity of furanocoumarins isolated from Angelica dahurica [J]. Arch Pharm Res, 2006, 29(9): 741-745. |
 2015, Vol. 46
2015, Vol. 46


