2. 吉林农业科技学院, 吉林 吉林 132101
2. Jilin Agricultural Science and Technology College, Jilin 132101, China
五味子科(Schisandraceae)隶属于木兰目(Magnoliales),分为北五味子属Schisandra Michx.和南五味子属Kadsura Juss.。北五味子属约30种,主产于亚洲东部和东南部,仅1种产美国东南部,我国有19种,南北各地均有分布;南五味子属28种,主产于亚洲东部和东南部,我国有10种,产于东南部至西南部[1]。
五味子科植物的主要成分为木脂素、三萜、挥发油、多糖等。其中主要的药效成分为木脂素,具有保肝、抑制中枢神经、抗氧化、抗衰老、抗肿瘤等多种药理活性[2]。然而近年来,尤其是孙汉董课题组发现了许多结构新颖、高度氧化且骨架重排的降三萜,二降三萜、三降三萜、五降三萜及八降三萜等多种新骨架的降三萜类化合物,同时药理活性实验表明其具有抗HIV和抗肿瘤等多种药理活性。
从五味子科植物中分到的三萜类化合物主要包括3种类型,羊毛脂烷型[3]、环阿屯烷型[4]和降三萜[5]。本文综述了国内外学者对五味子科植物中的降三萜类化合物的研究进展。
1 化学成分 1.1 Schisanartane型降三萜(I)此类型三萜化合物的结构特征:环阿屯烷型骨架的C-9,10位断裂形成七元环(C),C-16与C-17之间经特殊氧化断裂形成八元环(D)和五元环(F),C-9与C-15之间形成氧桥环(E),同时C-28缺失,目前分离的降三萜类化合物绝大部分属于此类型(1~77),并且均是从北五味子属植物中发现得到的,因此命名为schisanartane降三萜。此类型降三萜化合物又分为以下5个亚类:(1)C-1、C-2、C-3与C-10形成五元内酯环(A),C-1、C-4、C-5、C-10形成呋喃环(B),C-15、C-16、C-22、C-23及C-24形成吡喃环(G),C-22、26内酯环(H),目前分离得到的schisanartane型降三萜化合物大部分属于此类型,共分离得到此类成分37个(1~37);(2)C-1位H被-OH取代,其余同(1),属于此类型的降三萜化合物共9个(38~46);(3)A环开裂,其余同(1),属于此类型的降三萜化合物共11个(47~57);(4)G环开裂,其余同(1),属于此类型的降三萜化合物共9个(58~66);(5)其他的schisanartane型化合物共11个(67~77)。具体见图 1和表 1。
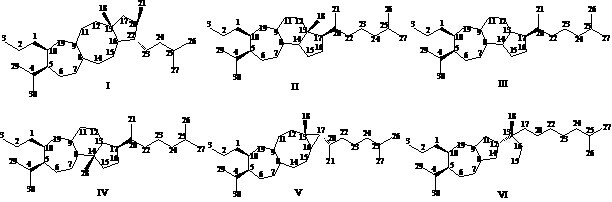
|
降三萜的结构母核 Fig. 1 Skeletons of nortriterpenoids |
|
|
表 1 降三萜类化合物 Table 1 Nortriterpenoids |
此类型三萜化合物的结构特征:环阿屯烷型骨架的C-9,10位断裂形成七元环(C),C-28缺失,侧链常形成C-22,26内酯环或C-23,26内酯环。目前分离的此类型化合物大部分都是从北五味子属中分离得到的(78~86),但是从南五味子属植物冷饭团K. coccinea (Lam.) A. C. Smith和中泰南五味子K. ananosma A. C. Smith中分离得到4个此类型化合物(87~90),具体见图 1和表 1。
1.3 18-Norschiartane型降三萜(III)此类型三萜化合物的结构特征:环阿屯烷型骨架的C-9,10位断裂形成七元环(C),C-18和C-28缺失,侧链常形成C-23,26内酯环,与schiartane型降三萜相比,即C-18缺失,因此命名为18-norschiartane型降三萜。目前从该科植物共分离得到此种类型的化合物15个(91~105),其中绝大部分来自北五味子属植物,仅从冷饭团和K. ananosma中各分离得到1个(99、104),具体见图 1和表 1。
1.4 18(13→14)-abeo-Schiartane型降三萜(IV)
此类化合物的结构与schiartane型降三萜的差别:C-13上连接的C-18甲基转到C-14位,而且甲基的构型为β型,侧链常形成C-23,26内酯环,目前从该科植物共分离得到此种类型的化合物14个(106~119),具体见图 1和表 1。
1.5 Pre-schisanartane型降三萜(V)此类化合物的结构与schisanartane型降三萜的差别:C-13、C-16、C-17、C-20和C-22的五元碳环重排形成C-13、C-16、C-17三元碳环(F),从而构建了一个罕见的连续的8/3碳环系,此结构可能是schisanartane型降三萜生源合成的前体化合物,因此命名为pre-schisanartane型降三萜。目前从该科植物共分离得到此种类型的化合物17个(120~136),且均是从北五味子属植物中发现得到,具体见图 1和表 1。
1.6 Wuweiziartane型降三萜(VI)此类化合物的结构特征:环阿屯烷型骨架的C-9,10位断裂形成七元环(C),骨架改变形成的五元环(D,C-8、C-9、C-11、C-12、C-14),C-12,16形成六元内酯环(E),侧链常形成C-23,26内酯环,目前只从北五味子属植物中分离得到5个此类型化合物(137~141),具体见图 1和表 1。
2 药理作用 2.1 抗HIV作用Xiao等[8, 10, 25]从狭叶五味子中分得的化合物20-OH-micrandilactone D(3),lancifodilactone G、I~N(67、58~60、8、9、17),具有抗HIV活性,其EC50值分别为99.0、95.47、96.4、88.3、78.5、100.0、76.6、77.6 μg/mL;A环开裂的schisanartane型降三萜rubriflorin A~J(47~56)[22, 23]、wilsonianadi- lactone A(57)[15],除化合物rubriflorin E(51)量少没有测定外,均具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为10.0、16.2、81.3、19.1、87.1、95.5、15.5、15.8、19.1、23.5 μg/mL。Xiao等[26, 28]从华中五味子中分得的化合物sphenalactone A~D (68~71)和 sphenadilactone C(74),具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为89.1、74.1、52.5、35.5、29.5 μg/mL;Lin等[30]从台湾五味子中分得的化合物schinarisanlactone A(77)具有显著的抗HIV活性,当浓度为10 μmol/L时,其抑制率高达88.2%。Yang等[15]从鹤庆五味子中分得的化合物wilsonianadilactone B、C(29、30),具有抗HIV活性,其EC50值分别为55.5、66.4 μg/mL。Xiao等[16, 37]从红花五味子中分得的化合物schirubridilactone A~F(31~35、105)及rubriflordilactone B(93)具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为30.1、15.2、14.3、80.8、66.8、50.1、9.75 μg/mL。Li等[31]从小花五味子中分得的化合物micrandilactone C(79)具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为7.71 μg/mL。Huang等[18, 38, 44]从五味子中分得的化合物pre- schisanartanin A(120)、wuweizidilactone A、B(94、95)、schintrilactone A、B(137、138),具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为13.81、26.81、28.86、17.9、36.2 μg/mL。Gao等[43]从鹤庆五味子中得到的化合物schilancidilactone V、W(132、133),具有抗HIV的活性,其EC50值分别为3.05、2.87 μg/mL。
2.2 抗乙型肝炎病毒作用Lei等[40]从合蕊五味子中分得的propindilactone L(114),具有显著抑制乙肝表面抗原(HBsAg)和乙肝e抗原HBeAg的作用,这是首次报道降三萜具有抗乙型肝炎病毒的作用,而且疗效显著,其标准病床有效利用指数(SI)值分别为2.68、1.11。
2.3 抗炎作用Cheng等[21]从台湾五味子中分得的化合物arisanlactone B、D(46、136)具有温和的抗炎作用,浓度为10 μg/mL时对弹性蛋白酶的抑制率分别为22.24%和18.47%。
2.4 抗肿瘤作用Gao等[43]从鹤庆五味子中分得的化合物schilancidilactone V(132),对口腔上皮癌细胞KB和乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231细胞具有明显的细胞毒活性,其IC50值分别为3.18、5.22 μmol/L。
3 结语降三萜类成分是一类结构新颖、高度氧化且骨架重排的三萜类化合物,是五味子科中常见的三萜类化合物之一。50多年来,国内外学者对该科植物的化学成分及生物活性的研究非常活跃,得到了系列三萜和木脂素类化合物,尤其是孙汉董课题组对降三萜的研究尤为突出,发现了许多新颖的降三萜骨架。这些新的萜类化合物的发现以及药理活性的研究,不仅丰富了三萜类化合物的内容,而且加深了对五味子科植物化学成分的认识,促进了五味子科植物次生代谢成分的研究,为进一步合理开发利用五味子科药用植物资源提供了新的化学物质基础。
| [1] | 中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 中国植物志 (30卷第1分册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996. |
| [2] | 史 琳, 王志成, 冯叙桥. 五味子化学成分及药理作用的研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究, 2011, 34(3): 208-212. |
| [3] | 金银萍, 焉 石, 刘俊霞, 等. 五味子科植物中羊毛脂烷型三萜类成分及其药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2014, 45(1): 137-143. |
| [4] | 金银萍, 焉 石, 刘俊霞, 等. 五味子科植物中环阿屯烷型三萜类成分及其药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2014, 45(4): 582-589. |
| [5] | Xiao W L, Li R T, Huang S X, et al. Triterpenoids from the Schisandraceae family[J]. Nat Prod Rep, 2008, 25: 871-891. |
| [6] | Li R T, Zhao Q S, Li S H, et al. Micrandilactone A: A novel triterpene from Schisandra micrantha[J]. Org Lett, 2003, 5(7): 1023-1026. |
| [7] | Li R T, Xiao W L, Shen Y H, et al. Structure characterization and possible biogenesis of three new families of nortriterpenoids: schisanartane, schiartane, and 18-norschiartane[J]. Chem Eur J, 2005, 11: 2989-2996. |
| [8] | Xiao W L, Yang L M, Zhang H B, et al. Chemical constituents from the leaves and stems of Schisandra lancifolia[J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 2010, 58(6): 852-855. |
| [9] | Li R T, Xiang W, Li S H, et al. Lancifodilactones B—E, new nortriterpenes from Schisandra lancifolia[J]. J Nat Prod, 2004, 67: 94-97. |
| [10] | Xiao W L, Huang S H, Zhang L, et al. Nortriterpenoids from Schisandra lancifolia[J]. J Nat Prod, 2006, 69: 650-653. |
| [11] | Xiao W L, Wu Y L, Shang S Z, et al. Four new nortriterpenoids from Schisandra lancifolia[J]. Helv Chim Acta, 2010, 93: 1975-1982. |
| [12] | Li R T, Shen Y H, Xiang W, et al. Four novel nortriterpenoids isolated from Schisandra henryi var. yunnanensis[J]. Eur J Org Chem, 2004, 4: 807-811. |
| [13] | Lei C, Huang S X, Chen J J, et al. Four new schisanartane-type nortriterpenoids from Schisandra propinqua var. propinqua[J]. Helv Chim Acta, 2007, 90: 1399-1405. |
| [14] | Lei C, Huang S X, Xiao W L, et al. Schisanartane nortriterpenoids with diverse post-modifications from Schisandra propinqua[J]. J Nat Prod, 2010, 73: 1337-1343. |
| [15] | Yang G Y, Xiao W L, Chang Y, et al. Nortriterpenoids from Schisandra wilsoniana[J]. Helv Chim Acta, 2008, 91: 1871-1878. |
| [16] | Xiao W L, Yang S Y, Yang L M, et al. Chemical constituents from the leaves and stems of Schisandra rubriflora[J]. J Nat Prod, 2010, 73: 221-225. |
| [17] | He F, Li X Y, Yang G Y, et al. Nortriterpene constituents from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Tetrahedron, 2012, 68: 440-446. |
| [18] | Huang S X, Li R T, Liu J P, et al. Isolation and characterization of biogenetically related highly oxygenated nortriterpenoids from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Org Lett, 2007, 9(11): 2079-2082. |
| [19] | Huang S X, Han Q B, Lei C, et al. Isolation and characterization of miscellaneous terpenoids of Schisandra chinensis[J]. Tetrahedron, 2008, 64: 4260-4267. |
| [20] | Xue Y B, Zhang Y L, Yang J H, et al. Nortriterpenoids and lignans from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis[J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 2010, 58(12): 1606-1611. |
| [21] | Cheng Y B, Liao T C, Lo Y W, et al. Nortriterpene lactones from the fruits of Schisandra arisanensis[J]. J Nat Prod, 2010, 73: 1228-1233. |
| [22] | Xiao W L, Li X L, Wang R R, et al. Triterpenoids from Schisandra rubriflora[J]. J Nat Prod, 2007, 70: 1056-1059. |
| [23] | Xiao W L, Pu J X, Wang R R, et al. Isolation and structure elucidation of nortriterpenoids from Schisandra rubriflora[J]. Helv Chim Acta, 2007, 90: 1505-1513. |
| [24] | Lei C, Huang S X, Xiao W L, et al. Schisanartane nortriterpenoids with diverse post-modifications from Schisandra propinqua[J]. J Nat Prod, 2010, 73: 1337-1343. |
| [25] | Xiao W L, Zhu H J, Shen Y H, et al. Lancifodilactone G: A unique nortriterpenoid isolated from Schisandra lancifolia and its anti-HIV activity[J]. Org Lett, 2005, 7(11): 2145-2148. |
| [26] | Xiao W L, Yang L M, Li L M, et al. Sphenalactones A-D, a new class of highly oxygenated trinortriterpenoids from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2007, 48: 5543-5546. |
| [27] | Xiao W L, Pu J X, Chang Y, et al. Sphenadilactones A and B, two novel nortriterpenoids from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Org Lett, 2006, 8(7): 1475-1478. |
| [28] | Xiao W L, Huang S X, Wang R R, et al. Nortriterpenoids and lignans from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Phytochemistry, 2008, 69: 2862-2866. |
| [29] | Lei C, Huang S X, Xiao W L, et al. Schisanartane nortriterpenoids with diverse post-modifications from Schisandra propinqua[J]. J Nat Prod, 2010, 73: 1337-1343. |
| [30] | Lin Y C, Lo I W, Chen S Y, et al. Schinarisanlactone A, a new bisnortriterpenoid from Schisandra arisanensis[J]. Org Lett, 2011, 13(3): 446-449. |
| [31] | Li R T, Han Q B, Zheng Y T, et al. Structure and anti-HIV activity of micrandilactones B and C, new nortriterpenoids possessing a unique skeleton from Schisandra micrantha[J]. Chem Commun, 2005, 23: 2936-2938. |
| [32] | Wang J R, Zhao Z B, Guo Y W. A new highly oxygenated nortriterpenoid from Schisandra chinensis[J]. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2011, 13(6): 551-555. |
| [33] | Lei C, Huang S X, Chen J J, et al. Propindilactones E—J, schiartane nortriterpenoids from Schisandra propinqua var. propinqua[J]. J Nat Prod, 2008, 71: 1228-1232. |
| [34] | Gao X M, Pu J X, Huang S X, et al. Kadcoccilactones A—J, triterpenoids from Kadsura coccinea[J]. J Nat Prod, 2008, 71: 1182-1188. |
| [35] | Yang J H, Wen J, Du X, et al. Triterpenoids from the stems of Kadsura ananosma[J]. Tetrahedron, 2010, 66: 8880-8887. |
| [36] | Li R T, Li S H, Zhao Q S, et al. Lancifodilactone A, a novel bisnortriterpenoid from Schisandra lancifolia[J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 2003, 44: 3531-3534. |
| [37] | Xiao W L, Yang L M, Gong N B, et al. Rubriflordilactones A and B, two novel bisnortriter-penoids from Schisandra rubriflora and their biological activities[J]. Org Lett, 2006, 8(5): 991-994. |
| [38] | Huang S X, Yang L B, Xiao W L, et al. Wuweizidilactones A—F: novel highly oxygenated nortriterpenoids with unusual skeletons isolated from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Chem Eur J, 2007, 13: 4816-4822. |
| [39] | Lei C, Huang S X, Xiao W L, et al. Bisnortriterpenoids possessing an 18-nor-schiartane skeleton from Schisandra propinqua var. propinqua[J]. Planta Med, 2010, 76: 1611-1615. |
| [40] | Lei C, Pu J X, Huang S X, et al. A class of 18(13→14)-abeo-schiartane skeleton nortriterpenoids from Schisandra propinqua var. propinqua[J]. Tetrahedron, 2009, 65: 164-170. |
| [41] | Lei C, Xiao W L, Huang S X, et al. Pre-schisanartanins C—D and propintrilactones A-B, two classes of new nortriterpenoids from Schisandra propinqua var. propinqua[J]. Tetrahedron, 2010, 66: 2306-2310. |
| [42] | 罗 晓. 三种药用植物的化学成分和生物活性研究[D]. 昆明: 中国科学院昆明植物研究所, 2009. |
| [43] | Gao X M, Li Y Q, Shu L D, et al. New triterpenoids from the fruits of Schisandra wilsoniana and their biological activities[J]. Bull Korean Chem Soc, 2013, 34(3): 827-830. |
| [44] | Huang S X, Yang J, Huang H, et al. Structural characterization of schintrilactone, a new class of nortriterpenoids from Schisandra chinensis[J]. Org Lett, 2007, 9(21): 4175-4178. |
| [45] | Jiang Y, Yang G Z, Chen Y, et al. Terpenes from Schisandra sphenanthera[J]. Helv Chim Acta, 2011, 94: 491-496. |
 2014, Vol. 45
2014, Vol. 45


