2. 南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院 药学部, 江苏 南京 210008
2. Department of Pharmacy, Affliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, China
九里香Murraya exotica L.为芸香科九里香属植物,主要分布在我国云南、贵州、湖南、广东、广西、福建、海南、台湾等省区,以及亚洲一些热带及亚热带地区,其气香,味苦、辛,有麻舌感,具有行气止痛、活血散瘀之功效,用于胃痛、风湿痹痛,也用于治疗牙痛、跌扑肿痛、虫蛇咬伤。很早以前,我国南方就将九里香作为一种民间用药,用于治疗各种病症,特别是炎性病变和镇痛[1]。目前,已从九里香中分离出香豆素类、黄酮类、挥发油类、生物碱类等化学成分[2, 3, 4]。现代药理研究表明,九里香具有抗菌、消炎镇痛、杀虫及抗氧化等作用[5, 6]。本文综述了九里香化学成分和药理作用的研究进展,为其药效物质基础、作用机制研究及开发利用提供了理论依据。
1 化学成分近年来,中外学者对九里香的化学成分进行了大量研究,从其叶、根皮、果实等部位中分离得到了多种化合物,主要包括香豆素类、黄酮类、生物碱类以及挥发油等。
1.1 香豆素类九里香含有大量的香豆素类成分(1~36),这类成分的常见特征为在7-甲氧基或5,7-二甲氧基香豆素骨架的C8位带有异戊二烯单位,以氧化、酯化或骨架重排等多种形式存在。见表 1、图 1。
| 表 1 九里香香豆素类化学成分 Table 1 Coumarin constituents in M. exotica |
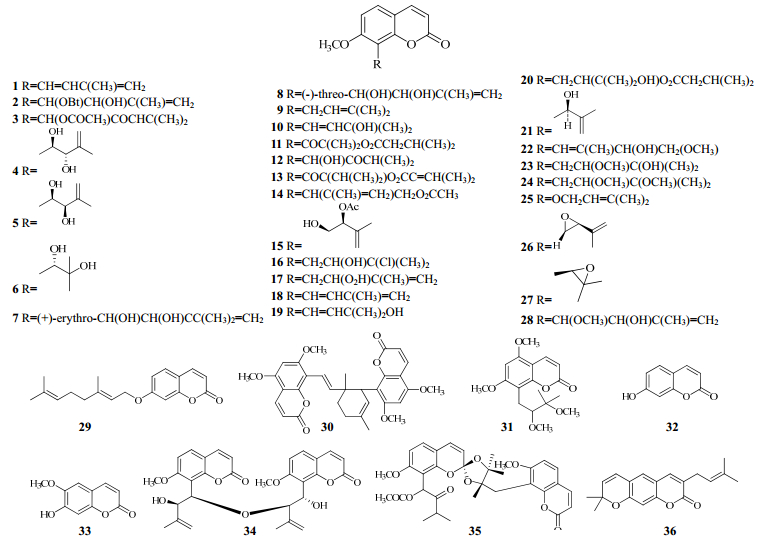 | 图 1 九里香香豆素类化学成分的结构 Fig.1 Structures of coumarin constituents in M. exotica |
九里香含有多种黄酮类化合物(37~55),还含有5,3'-dihydroxy-6,4'-dimethoxyflavone-7-O-β-D- glucopyranoside、5,3'-dihydroxy-6,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone- 8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside黄酮苷类成分[22]。九里香中的黄酮类化学成分见表 2、图 2。
| 表 2 九里香黄酮类化学成分 Table 2 Flavone constituents in M. exotica |
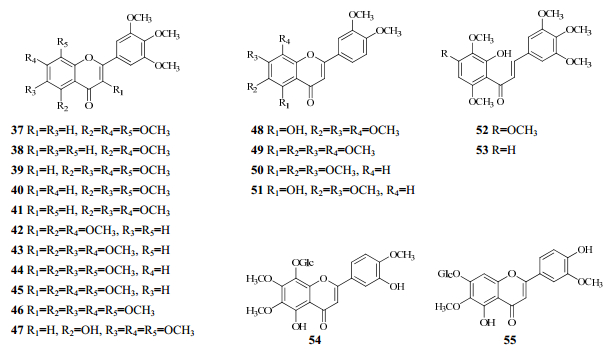 | 图 2 九里香黄酮类化学成分的结构 Fig.2 Structures of flavone constituents in M. exotica |
九里香的叶中含有大量的黄酮类和香豆素类化合物,而九里香的根、皮中主要含有生物碱类成分。其生物碱类成分(56~64)见表 3,结构见图 3。
| 表 3 九里香生物碱类化学成分 Table 3 Alkaloid constituents of M. exotica |
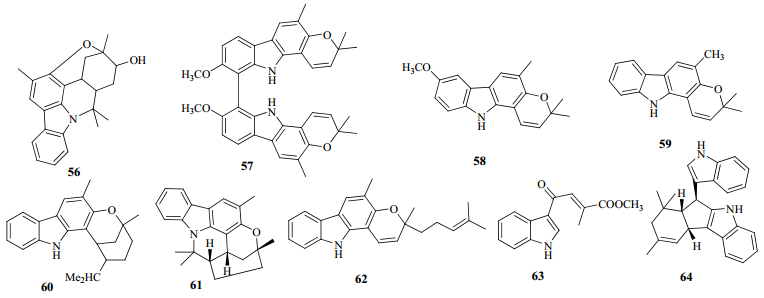 | 图 3 九里香生物碱类化学成分的结构 Fig.3 Structures of alkaloid constituents in M. exotica |
挥发油类是九里香的主要化学成分之一。其挥发油成分的含量因品种、采收季节、地区不同而存在差异,含量的高低影响九里香的药材质量及临床疗效。其挥发油类成分(65~95)见表 4。
| 表 4 九里香挥发油类化学成分 Table 4 Volatile oil constituents in M. exotica |
Bishay等[11]还从九里香叶中分离得到了羽扇豆醇;Ahmad等[39]从九里香叶中分离出了柯伦氏泪柏烯酮和柯伦氏泪柏酮;Kong等[40]、Das等[41]分别从九里香树皮中分离得到了金色酰胺醇酯。
2 药理作用 2.1 杀虫作用Li等[34]研究发现九里香地上部分具有杀虫活性,能够杀死玉米象虫和赤拟谷盗虫。卢远倩等[42]采用生物活性追踪和化学分离相结合的方法,发现九里香氯仿萃取物对家蝇成虫、斜纹夜蛾、萝卜蚜、椰心叶甲有杀灭作用。Tiwari等[43]在实验室条件下,研究保幼激素类似物对致倦库蚊幼虫死亡率的影响,将3%九里香叶丙酮提取液局部作用于致倦库蚊三龄幼虫,会导致其100%的死亡率,随着丙酮提取液浓度的降低,幼虫死亡率减小。Kishnamoorthy等[37]研究了九里香叶挥发油的化学组成及其对埃及斑蚊、斯氏按蚊、致倦库蚊的杀灭效果,分别在12、24 h后观察九里香叶挥发油的杀虫活性。实验结果显示九里香叶挥发油对埃及斑蚊、斯氏按蚊、致倦库蚊表现出不同程度的杀虫能力。12 h后,其埃及斑蚊的半数致死浓度(LC50)、LC90分别为74.7、152.7 mg/L,斯氏按蚊的LC50、LC90分别为56.3、107.8 mg/L,致倦库蚊的LC50、LC90分别为74.4、136.9 mg/L;而24 h后,埃及斑蚊的LC50、LC90分别为35.8、85.4 mg/L;斯氏按蚊的LC50、LC90分别为31.3、75.1 mg/L;致倦库蚊的LC50、LC90分别为43.2、103.2 mg/L。结果表明九里香叶挥发油有望成为杀灭埃及斑蚊、斯氏按蚊、致倦库蚊经济有效的天然杀虫药。Sharma等[8]在研究臭节草中含有杀虫活性的香豆素时,分离得到murraxocin,而这一结构也从九里香中分离得到过。经评估,使用1.0%~5.0% murraxicin浓缩物能杀死大量森林害虫,如Plecoptera reflexa、周蛾和竹弯茎野螟。1% murraxocin对这些害虫有80%的致死率,并且其死亡率以剂量相关性的方式增大。
2.2 消炎镇痛作用Wu等[44]、吴龙火等[45, 46]以小鼠醋酸扭体实验和二甲苯致小鼠耳肿胀实验,对九里香的体内消炎镇痛活性进行了研究,结果表明,其70%乙醇提取物能明显降低醋酸导致的扭体反应,延长热板反应潜伏期,有效地抑制二甲苯致耳肿胀和角叉菜胶致脚肿胀。Wu等[47]还探究了九里香对骨关节炎的治疗效果,建立了小鼠骨关节炎模型,分为多个剂量(50、100、200 mg/kg)组给药,然后分离出小鼠体内炎性软骨细胞、滑液及血清,发现九里香能以剂量相关性的方式减少滑液及炎性软骨细胞中肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)和白细胞介素(IL-1β)的量。为了探讨可能的机制,他们采用定量实时酶聚合链反应和蛋白印迹法分别追踪基因和蛋白表达方式。实验结果表明,九里香可以抑制mRNA和蛋白表达,可能是通过抑制β-连环蛋白信号而表现出抗软骨细胞凋亡的活性。Lv等[1]对比分析从千里香M. paniculata和M. exotica中分离得到的挥发油成分,两者均含有E-caryophyllene,其对于治疗炎性病变和局部麻醉有重要作用。另有研究发现,九里香中分离得到的murracarpin的消炎镇痛活性很强,可能与其C7位上的甲氧基,C8位上一个短的支链含有双键及醇羟基等结构有关[2]。
2.3 抗菌作用Huang等[5]对我国海南九里香挥发油的抗菌活性进行了研究,发现九里香挥发油对除绿脓杆菌外的各种细菌均具有广泛的抗菌能力,且具有一定的抗真菌作用。El-Sakhawy等[48]研究了九里香挥发油的组成及抗菌能力,结果表明九里香挥发油对白色念珠菌表现出很强的抗菌活性,对大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌、金色葡萄球菌以及藤黄八叠球菌也有一定的抗菌作用。卢远倩等[49]采用生长速率法发现不同浓度九里香萃取物和精油对各种病菌的抑制效果不同。
2.4 抗氧化作用Huang等[5]对我国海南九里香挥发油进行研究,九里香中含有97.76%的挥发油成分,特别是caryophyllene的量达到了45.51%。抗氧化活性测试表明,九里香中挥发油具有清理自由基的能力(IC50为151.1 mmol/L),从而达到抗氧化效果。
3 结语目前人们已从九里香中分离出香豆素类、黄酮类、生物碱类等活性成分。九里香不仅有杀虫、消炎镇痛、抗菌及抗氧化等作用,此外也有活血散瘀、祛风除湿等药理作用。现今九里香已在临床用于局部麻醉及表面麻醉,可以以九里香注射液进行局部麻醉,并且九里香药物的镇痛时间长,但仍存在局部刺激较大的缺点。九里香化学成分复杂,药理作用广泛,应加强对九里香的药理作用研究,尝试其与其他中药的配伍,以达到最优化治疗效果。
| [1] | Lv H N, Guo X Y, Tu P F, et al. Comparative analysis of the essential oil composition of Murraya paniculata and M. exotical [J]. Nat Prod Commun, 2013, 8(10): 1473-1475. |
| [2] | 吴龙火, 刘昭文, 曾 靖, 等. 九里香叶中香豆素类化合物的抗炎镇痛活性 [J]. 光谱实验室, 2011, 28(6): 2999-3003. |
| [3] | 彭爱一, 曲学伟, 李 慧, 等. 高速逆流色谱分离纯化九里香中的黄酮类化合物 [J]. 色谱, 2010, 28(4): 383-387. |
| [4] | 姜平川, 周 军, 曹 斌, 等. 九里香挥发油成分研究 [J]. 中药材, 2009, 32(8): 1224-1227. |
| [5] | Huang Y S, Wang Y, Luo X P, et al. Composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the essential oil of Murraya exotica from Hainan of China [J]. Asian J Chem, 2013, 25(9): 5055-5058. |
| [6] | 王三龙, 蔡 兵, 崔承彬, 等. 吉九里香碱诱导K562细胞凋亡的研究 [J]. 中草药, 2007, 38(11): 1677- 1681. |
| [7] | Kinoshita T. A new taxonomic system of the genus Murraya (Rutaceae) based on integration of morphology- based taxonomy and chemotaxonomy; and a philological survey on M. exotica in view of the relationship between Okinawa and China [J]. Yakugaku Zasshi, 2014, 134(12): 1265-1286. |
| [8] | Sharma R, Negi D S, ShiuW K, et al. Characterization of an insecticidal coumarin from Boenninghausenia albiflora [J]. Phytother Res, 2006, 20(7): 607-609. |
| [9] | Negi N, Ochi A, Kurosawa M, et al. Two new dimeric coumarins isolated from Murraya exotica [J]. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo), 2005, 53(9): 1180-1182. |
| [10] | Bishay D W, El-Sayyad S M, Abd El-Hafiz M A, et al. Phytochemical study of Murraya exotica L. cultivated in Egypt. II. coumarins of the leaves [J]. Bull Pharm Sci, 1988, 11(1): 88-104. |
| [11] | Bishay D W, El-Sayyad S M, Abdel-Hafiz M A, et al. Phytochemical study of Murraya exotica L. cultivated in Egypt. III. coumarins and cycloartenols of the leaves [J]. Bull Pharm Sci, 1988, 11(1): 105-121. |
| [12] | Ito C, Furukawa H. Two new coumarins from Murraya plants [J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1989, 37(3): 819-820. |
| [13] | Ito C, Furukawa H. Constituents of Murraya exotica L. Structure elucidation of new coumarins [J]. Chem Pharm Bull, 1987, 35(10): 4277-4285. |
| [14] | Ito C, Furukawa H. Three new coumarins from Murraya exotica [J]. Heterocycles, 1987, 26(7): 1731-1734. |
| [15] | Barik B R, Dey A K, Chatterjee A. Murrayatin, a coumarin from Murraya exotica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1983, 22(10): 2273-2275. |
| [16] | Barik B R, Dey A K, Das P C, et al. Coumarins of Murraya exotica. absolute configuration of auraptenol [J]. Phytochemistry, 1983, 22(3): 792-794. |
| [17] | Manandhar M D. 8-Substituted 7-methoxycoumarins from Murraya exotica Linn [J]. Indian J Chem, 1980, 19B(11): 1006-1008. |
| [18] | Lakshmi M V, Ratnam C V, Rao N V S. 7-Methoxy-8-(3- butenyl-3-methyl-2-oxo)-coumarin, a new coumarin from Murraya exotica [J]. Indian J Chem, 1972, 10(5): 564- 565. |
| [19] | Chakraborty D P, Roy S, Chakraborty A, et al. Structure and synthesis of mexolide, a new antibiotic dicoumarin from Murraya exotica Linn.[Syn. M. Paniculata (L)Jack.] [J]. Tetrahedron, 1980, 36(24): 3563-3564. |
| [20] | Chakraborty D P, Chowdhury B K, Das B. Mexoticin, a new coumarin from Murraya exotica L. [J]. Tetrahedron Lett, 1967, 8(36): 3471-3473. |
| [21] | Ahmad Z A, Begum S. 3-(1,1-Dimethylallyl)xanthyletin from Murraya exotica [J]. Indian Drugs, 1986, 24(1): 64. |
| [22] | Zhang J Y, Lu J, Zhang Q, et al. Simultaneous screening and identifying four categories of particular flavonoids in the leaves of Murraya exotica L. by HPLC-DAD-ESI- MS-MS [J]. J Chromatogr Sci, 2014, 52(2): 103-114. |
| [23] | Desoky E K. Phytochemical study of Murraya exotica L. (Rutaceae) growing in Egypt: methoxylated flavones [J]. Bull Fac Pharm, 1992, 30(3): 287-292. |
| [24] | Bishay D W, El-Sayyad S M, Abd El-Hafiz M A, et al. Phytochemical study of Murraya exotica L. (Rutaceae). I-Methoxylated flavonoids of the leaves [J]. Bull Pharm Sci, 1987, 10(2): 55-70. |
| [25] | Joshi B S, Kamat V N. Isolation of 3,3',4',5,5',7,8- heptamethoxyflavone from Murraya exotica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1970, 9(4): 889. |
| [26] | Joshi B S, Kamat V N. Structure of exoticin, a flavone from the leaves of Murraya exotica [J]. Indian J Chem, 1969, 7(6): 636. |
| [27] | Ahmad Z A. Murrayazolinol from Murraya exotica [J]. Indian Drugs, 1994, 31(1): 32-33. |
| [28] | Desoky E K, Bishay D W. A new dimeric carbazole alkaloid from Murraya exotica L.(Rutaceae) cultivated in Egypt [J]. Bull Fac Pharm, 1992, 30(3): 231-233. |
| [29] | Desoky E K, Kanwl M S, Bishay D W. Alkaloids of Murraya exotica L. (Rutaceae) cultivated in Egypt [J]. Bull Fac Pharm, 1992, 30(3): 235-238. |
| [30] | Roy S, Bhattacharya L. Girinimbine and koenimbine from Murraya exotica Linn [J]. J Indian Chem Soc, 1981, 58(12): 1212. |
| [31] | Ganguly S N, Sarkar A. Exozoline, a new carbazole alkaloid from the leaves of Murraya exotica [J]. Phytochemistry, 1978, 17(10): 1816-1817. |
| [32] | Bhattacharyya P, Roy S, Biswas A, et al. Mahanimbine and murrayazoline from Murraya exotica Linn. (syn. Murraya paniculata) [J]. J Chem Soc, 1978, 55(3): 308. |
| [33] | Kong Y C, Cheng K F, Cambie R C, et al. Yuehchukene: a novel indole alkaloid with antiimplantation activity [J]. J Chem Soc, 1985(2): 47-48. |
| [34] | Li W Q, Jiang C H, Chu S S, et al. Chemical composition and toxicity against Sitophilus zeamais and Tribolium castaneum of the essential oil of Murraya exotica aerial parts [J]. Molecules, 2010, 15(8): 5831-5839. |
| [35] | Raina V K, Verma S C, Dhawan S, et al. Essential oil composition of Murraya exotica from the plains of northern India [J]. Flavour Fragran J, 2006, 21(1): 140-142. |
| [36] | Gupta U, Chandra G. Chemical constituents of the essential oil from the flowers of Murraya exotica [J]. Soap Perfum Cosmet, 1974, 47(2): 67-68. |
| [37] | Krishnamoorthy S, Chandrasekaran M, Raj G A, et al. Identification of chemical constituents and larvicidal activity of essential oil from Murraya exotica L. (Rutaceae) against Aedes aegypti, Anopheles stephensi and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) [J]. Parasitol Res, 2015, 114(5): 1839-1845. |
| [38] | Li W Q, Jiang C H, Chu S S, et al. Chemical composition and toxicity against Sitophilus zeamais and Tribolium castaneum of the essential oil of Murraya exotica aerial parts [J]. Molecules, 2010, 15(8): 5831-5839. |
| [39] | Ahmad Z A, Begum S. Colensenone and colensanone (non-diterpene oxide) from Murraya exotica Linn [J]. Indian Drugs, 1987, 24(6): 322. |
| [40] | Kong Y C, Ng K H, But P P, et al. Aurantiamide acetate in the stem bark of Murraya exotica [J]. Planta Med, 1987, 53(4): 393. |
| [41] | Das P C, Mandal S, Das A, et al. Aurantiamide acetate from Murraya exotica L. Application of two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy [J]. Indian J Chem, 1990, 29B(5): 495-497. |
| [42] | 卢远倩. 九里香农用活性研究及成分分析 [D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2012. |
| [43] | Tiwari O P, Saxena R C. Effect of a juvenile hormone analog on the larval mortality of Culex fatigans (Diptera: culicidae) [J]. Comp Physiol Ecol, 1984, 9(1): 54-55. |
| [44] | Wu L H, Li P, Wang X, et al. Evaluation of anti- inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Murraya exotica [J]. Pharm Biol, 2010, 48(12): 1344-1353. |
| [45] | 吴龙火, 温慧玲, 金 奇, 等. 九里香指纹图谱与其抗炎活性的灰关联度分析 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2013, 19(4): 338-342. |
| [46] | 吴龙火, 刘昭文, 许瑞安. 九里香叶的抗炎镇痛作用研究 [J]. 湖北农业科学, 2011, 50(21): 4435-4437. |
| [47] | Wu L H, Liu H Q, Zhang R, et al. Chondroprotective activity of Murraya exotica through inhibiting β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Evid Based Complementary Alternat Med, 2013, 2013: 752150. |
| [48] | El-Sakhawy F S, El-Tantawy M E, Ross S A, et al. Composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Murraya exotica L. [J]. Flavour Frag J, 1998, 13(1): 59-62. |
| [49] | 卢远倩, 王兰英, 骆焱平. 九里香精油的抑菌活性及成分分析 [J]. 农药, 2011, 50(6): 56-58. |
 2015, Vol. 30
2015, Vol. 30


